- Multi-source price discovery
- Real-time order matching
- Risk management modules
- Algo tools and technical indicators
EFX Trading: A Deep Dive into Electronic Forex Trading

EFX trading is transforming how modern traders approach the forex market. As an eFX trader, you benefit from real-time access, advanced automation, and flexible tools. Whether you're curious about what is eFX trading, or seeking to enter the eFX forex market with reliable strategies, this article covers all essentials.
“The future of forex is digital. EFX trading platforms not only offer speed, but data precision essential for institutional-grade decisions.” — Dr. Liam Harper, Financial Analyst at QuantEdge Markets
What is eFX Trading?
EFX trading refers to electronic forex trading conducted via digital systems rather than traditional phone-based brokerage. It leverages proprietary trading software, bots, and algorithms to automate trade execution with precision and speed. Through the integration of eFX Algo strategies, traders access real-time market data and minimize drawdowns. This method has enhanced market liquidity and allows seamless client trading performance monitoring.
| EFX Trading Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Electronic Execution | Fast and efficient trades |
| Secure Platform | Protected transactions |
| Automated Systems | Supports algo strategies |
| Real-Time Analytics | Data-driven decisions |
Core Components of eFX Trading Platforms
A robust eFX trading platform includes:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Trading Interface | Visual tools for entering and exiting trades |
| Order Types | Includes limit, market, stop, and conditional |
| Charting Features | Interactive analysis and forecasting |
| Integrated News | Financial updates impacting eFX forex |
Role of Brokers and Liquidity Providers
Brokers and liquidity providers play a central role in the eFX ecosystem. Brokers offer access to eFX trading platforms, facilitate transactions, and provide insights into client trading behavior. Liquidity providers such as banks and institutions ensure tight spreads and deep market access. Understanding the relationship between these actors is vital for developing effective fx trading strategies.
Best eFX Trading Platform Options
Traders evaluate eFX trading platform choices by their features, fees, and technology. Leading platforms include:
| Platform | Notable Tools |
|---|---|
| MetaTrader 5 | Advanced algo bot integration |
| cTrader | Direct market access with depth tools |
| TradingView | Visual charts with social login & bots |
How to Trade Forex with Micro Accounts on Pocket Option
Pocket Option makes it easy to trade Forex with small amounts — perfect for beginners or traders looking to manage risk with micro-sized positions. Whether you’re investing $1 per trade or testing a new strategy, you can access the global currency market through two flexible methods.
🕒 Option 1: Quick Forex Trading (OTC Available 24/7)
This built-in feature is ideal for fast, straightforward trades with minimal setup.
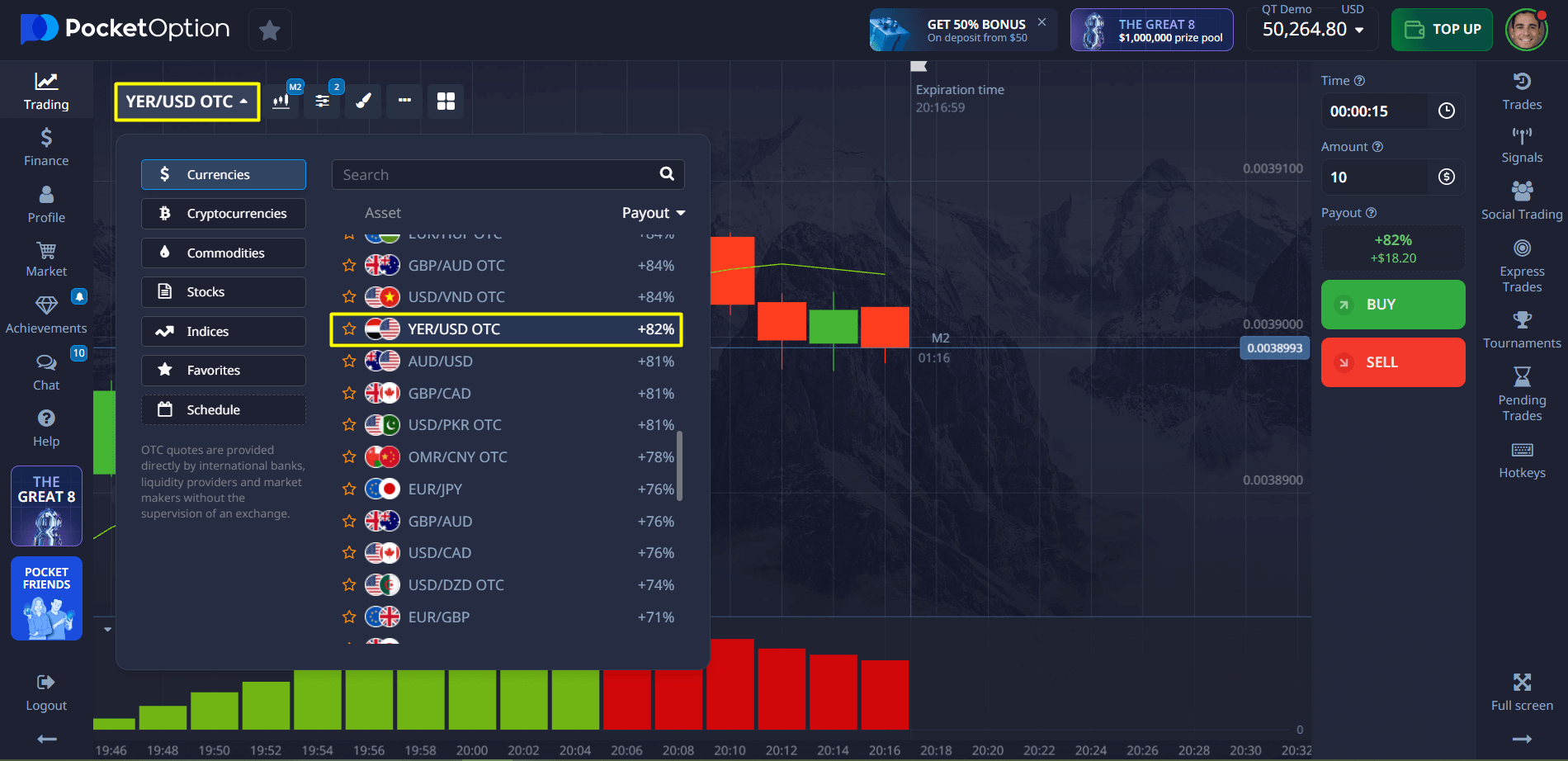
Steps to Trade:
- Log in to the Platform: Sign in to your Pocket Option account.
- Select Forex Assets: Choose “Forex” from the list of available instruments.
- Configure Your Trade: Start with as little as $1, set the duration, and choose the direction (up or down).
- Open the Trade: Predict the market movement and execute your trade.
- Track and Close: Monitor price action in real time. If your forecast is correct, earn up to 92% return.
This method is great for traders who value speed, ease of use, and round-the-clock availability — even on weekends, thanks to OTC Forex trading.
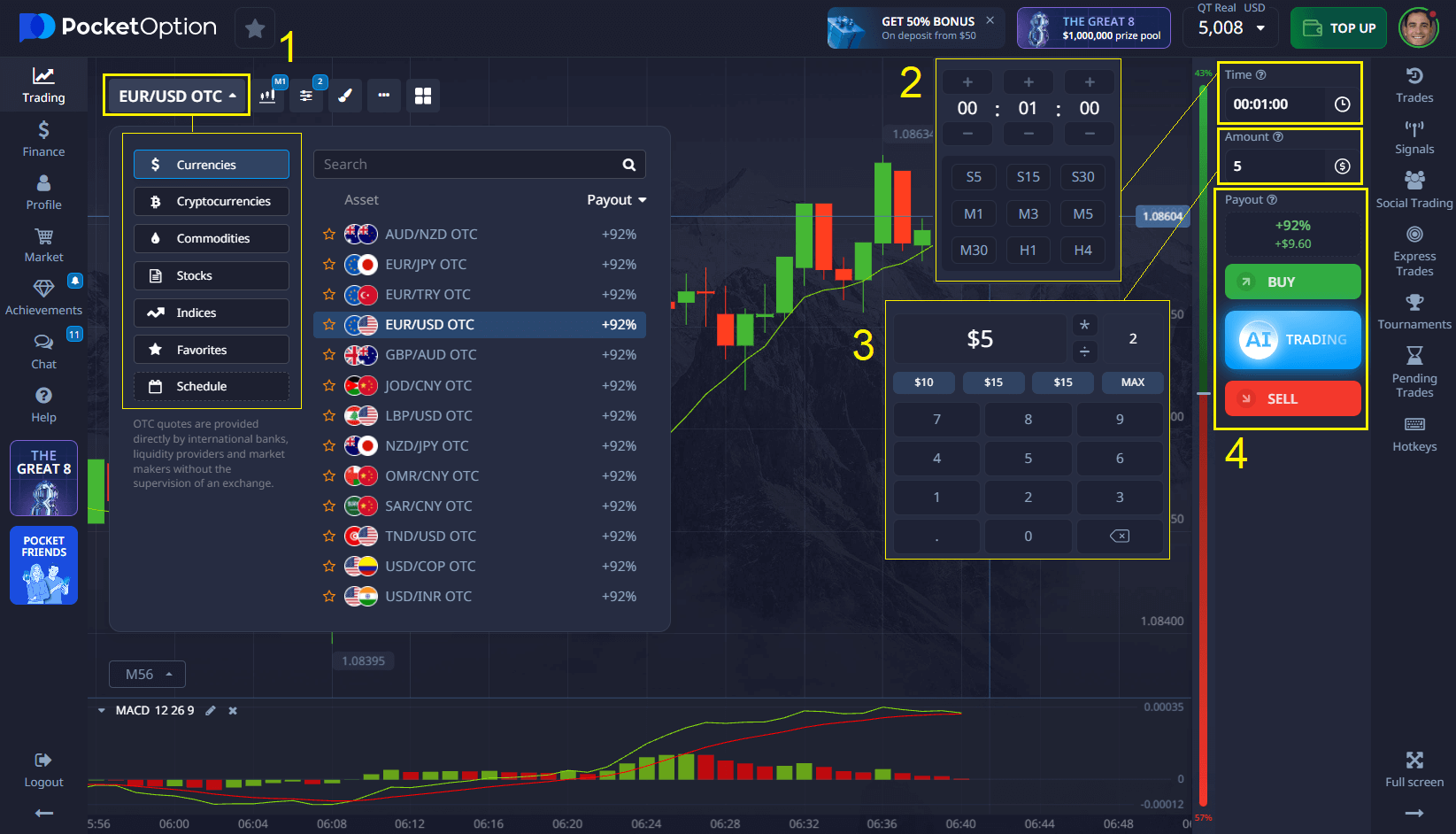
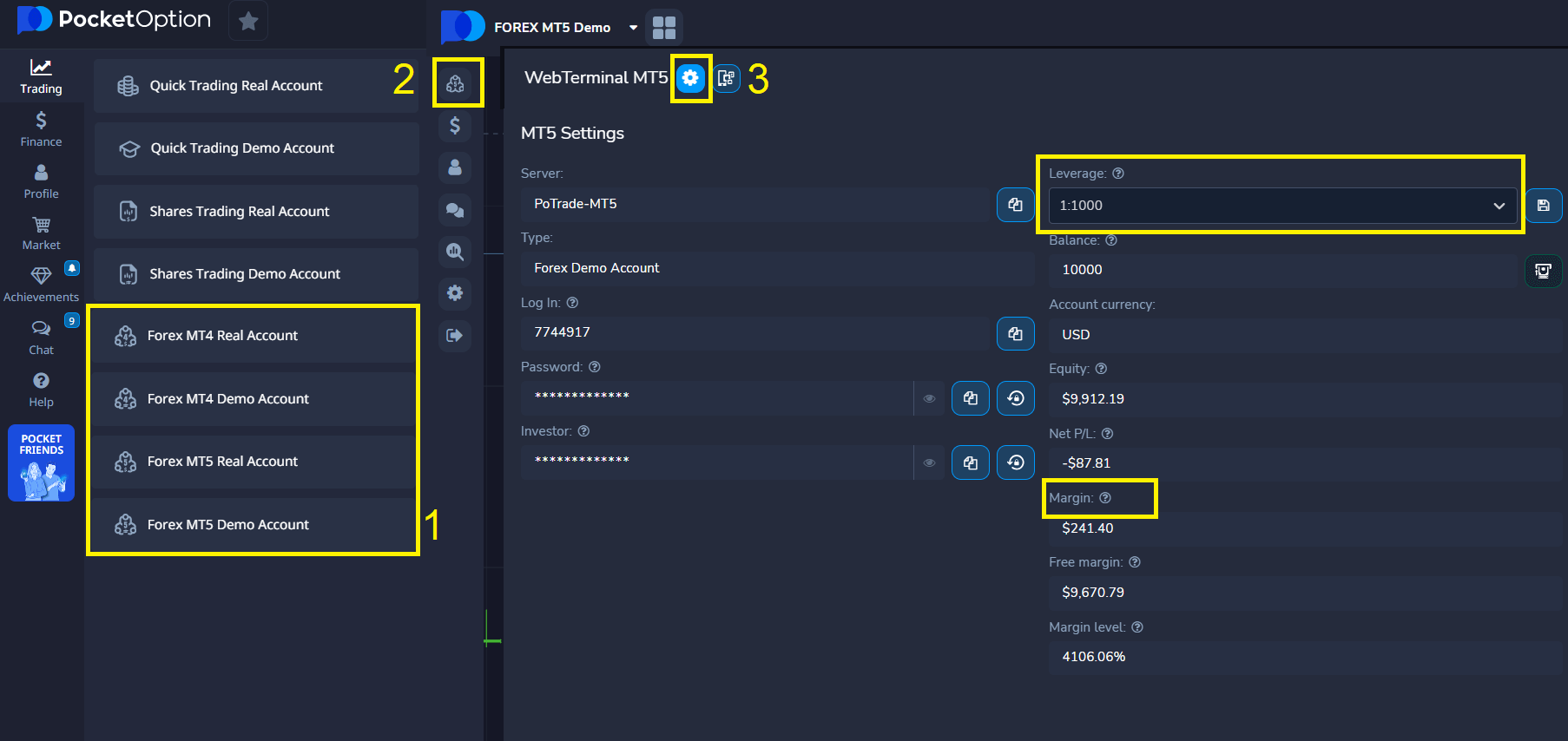
📊 Option 2: Advanced Forex Trading with MetaTrader 5 (MT5)
For traders seeking deeper analysis and professional tools, Pocket Option offers full access to the MetaTrader 5 (MT5) platform — the industry standard for Forex trading.
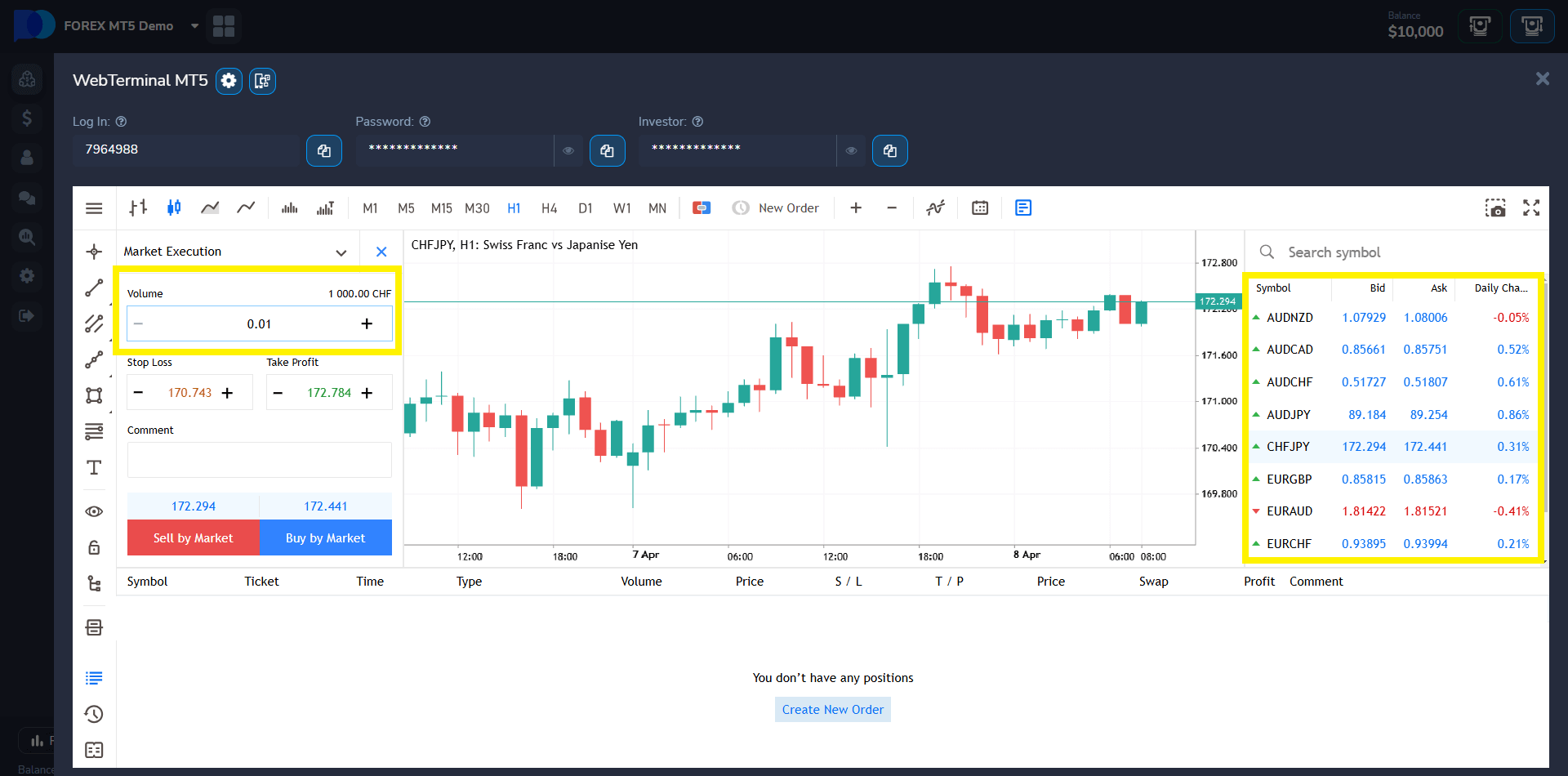
Steps to Get Started:
- Launch MT5: Open MetaTrader 5 through Pocket Option’s web or desktop interface.
- Log In: Use your Pocket Option MT5 credentials to access the terminal.
- Choose Currency Pairs: Trade a wide selection of Forex pairs, from major to exotic.
- Customize Trade Size and Leverage: Set micro-lots and adjust leverage up to 1:1000 for precise capital control.
- Analyze and Execute: Leverage advanced charting tools, technical indicators, and expert advisors to refine your strategy.
User Feedback:
“Pocket Option helped me transition from demo to real trading. The login process is easy, and their bots give me confidence. Highly recommended.” — David L., Trader
“As a former equities trader, I found Pocket Option surprisingly rich in eFX tools. It’s great for learning and scaling up.” — Aisha M., eFX Enthusiast
EFX Algorithms and Software
EFX trading software allows users to execute trades based on predefined rules using algorithmic models. These tools analyze price action, patterns, and historical data to identify opportunities. Traders can select eFX Algo models based on their goals, from high-frequency trading to low-risk automated strategies. The year of running the algo significantly improves its performance due to real-time feedback and optimization.
Popular eFX Trading Strategies
Understanding when and how to engage in eFX forex trading is key:
- Trend Following
- Range Trading
- Breakout Trading
- News Reaction Trading
Pro Insight:
“Most beginner losses come from chasing breakouts. Combine strategies with context and data — that’s the winning formula in eFX forex.” — Natalia Cruz, Strategy Coach
| Strategy | Best Used When |
|---|---|
| Trend Following | Strong market direction is visible |
| Range Trading | Market fluctuates within support/resistance |
| Breakout Trading | Price breaches consolidation zones |
| News-Based | Around high-impact economic releases |
Risk Control in eFX Forex Trading
Risk management in eFX trading requires:
- Precise position sizing
- Stop loss and take profit rules
- Monitoring asset correlations
- Stable reward-to-risk ratios
Unique Tip: Use the correlation matrix tools in platforms like Pocket Option to visualize exposure across currency pairs.
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Stop Loss | Limit downside risk |
| Take Profit | Lock in profits at a preset level |
| Position Sizing | Adjust exposure based on capital size |
| Correlation Checks | Reduce double exposure to similar markets |
Consistency and Performance Metrics
To generate consistent returns, traders must review:
- Win rate and risk-reward ratios
- Drawdown history
- Backtesting and live testing results
These metrics help refine your eFX Algo selection and measure fx trading efficiency.
Final Thoughts
EFX trading offers a dynamic entry into global forex through advanced digital platforms. As an eFX trader, combining foundational knowledge with bots and structured strategies leads to more effective outcomes. Don’t trade blindly — test strategies with demo tools, review bot performance, and stay updated. Join the discussion on eFX in our community!
FAQ
Is eFX a good investment?
EFX trading can be a good investment for those with a solid strategy and risk management approach. Its liquidity and technological edge make it attractive to both retail and institutional participants.
Is algo trading really working?
Yes, algorithmic trading (or "algo") is widely used in eFX forex trading. With proper setup, it enhances speed and reduces emotional decisions. However, it requires regular monitoring and optimization.
What is eFX vs FX?
FX stands for the broader forex (foreign exchange) market. EFX specifically refers to electronic trading within FX, offering faster and more transparent trade execution compared to traditional methods.
How much time should I dedicate to EFX trading daily?
The time commitment depends on your trading style. Day traders might spend several hours monitoring markets, while swing traders may need only 1-2 hours daily to analyze markets and set up trades. The key is consistency and quality of analysis rather than quantity of time.
What are the most common mistakes new EFX traders make?
Common mistakes include trading without a plan, risking too much capital per trade, overtrading, ignoring risk management, trading based on emotions rather than analysis, and not keeping a trading journal to track and learn from results.