Understanding the MSCI World Index
The MSCI World Index is designed to track the performance of stocks from developed markets, serving as a key tool for investors seeking to understand global equity trends. This index includes a diverse range of sectors and regions, allowing for a comprehensive analysis of market dynamics. By benchmarking portfolios to the MSCI World, firms can effectively gauge their performance against a broad spectrum of investable securities.
According to market data analyst Sarah Chen from Goldman Sachs: “The MSCI World Index captures approximately 85% of the free float-adjusted market capitalization across developed markets, making it the most widely followed international equity benchmark.”
What is the MSCI World Index?
The MSCI World Index is an equity index that includes companies from multiple developed markets, providing a representative overview of global stock performance. It is widely used by asset managers and investment firms to formulate strategies and assess market risks. With its extensive coverage, the index captures the movements of significant firms in regions such as Europe, Japan, Australia, and North America, making it an essential component of global capital markets.
Components of the MSCI World Index
The MSCI World Index comprises thousands of securities, with companies selected based on market capitalization and liquidity. This selection ensures that the index reflects the largest and most influential firms in developed markets. Each quarter, the index undergoes an MSCI rebalance, which may result in the addition or removal of specific stocks, thereby impacting overall portfolio allocations and investment strategies.
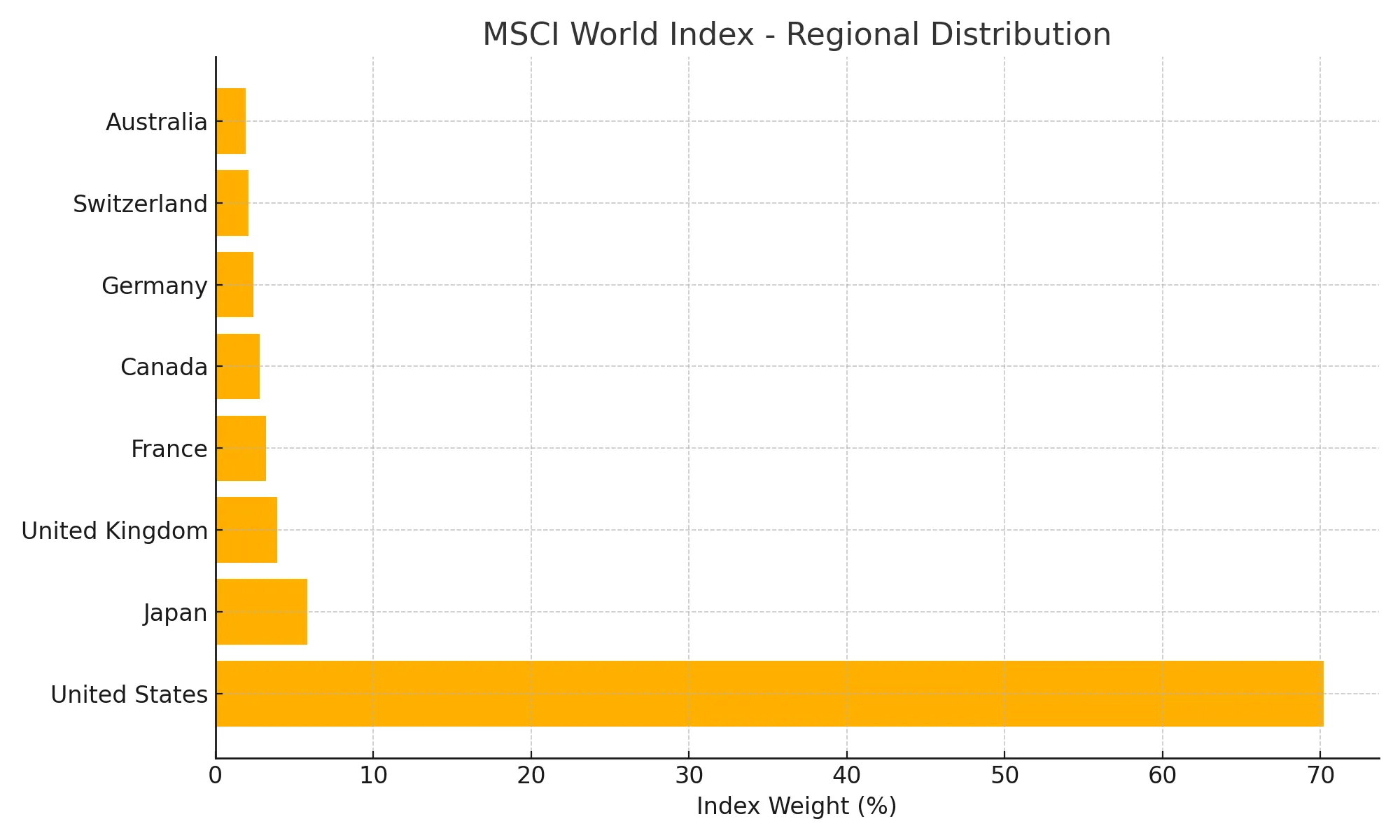
Key Regional Distribution:
| United States | 70.2% of total index weight |
| Japan | 5.8% |
| United Kingdom | 3.9% |
| France | 3.2% |
| Canada | 2.8% |
| Germany | 2.4% |
| Switzerland | 2.1% |
| Australia | 1.9% |
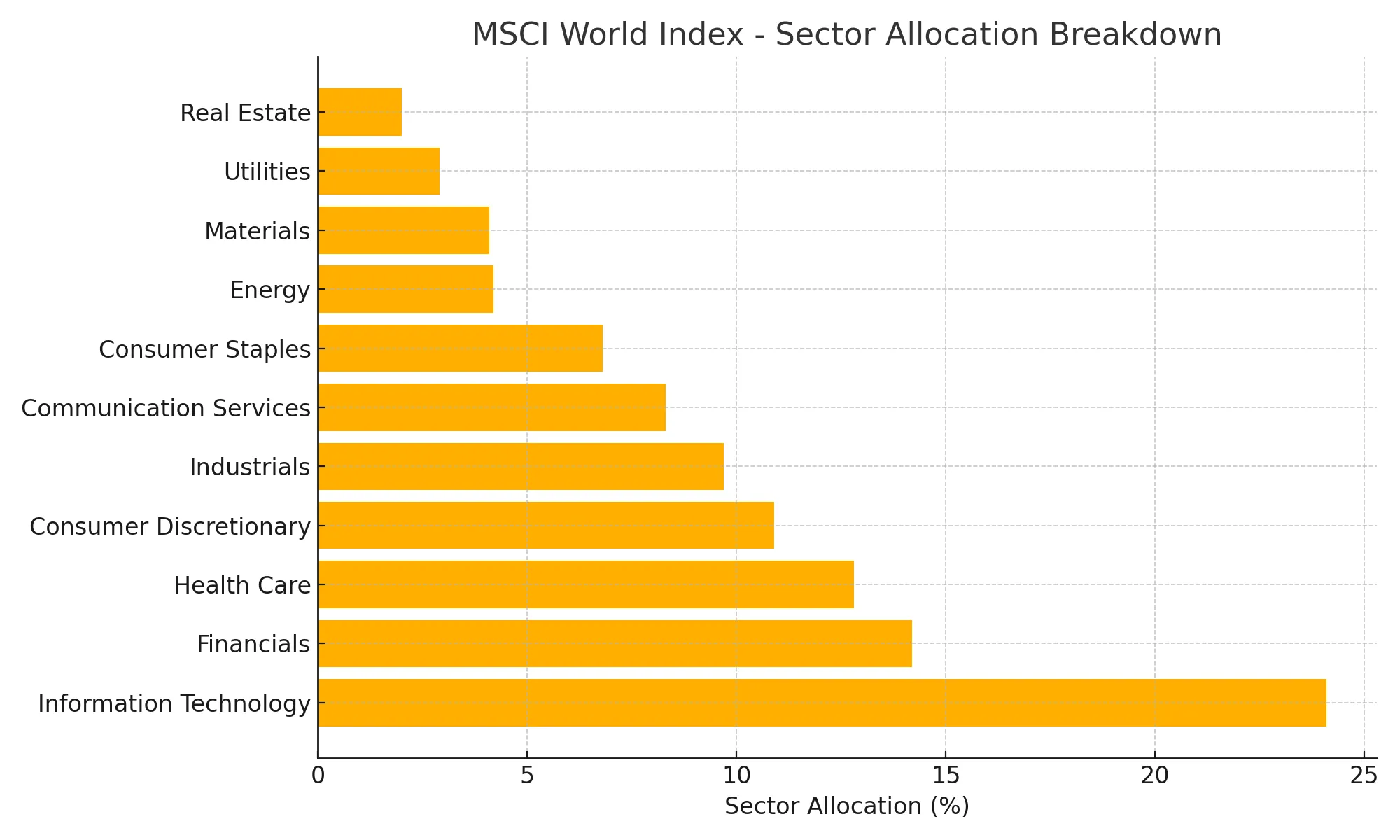
Sector Allocation Breakdown:
| Information Technology | 24.1% |
| Financials | 14.2% |
| Health Care | 12.8% |
| Consumer Discretionary | 10.9% |
| Industrials | 9.7% |
| Communication Services | 8.3% |
| Consumer Staples | 6.8% |
| Energy | 4.2% |
| Materials | 4.1% |
| Utilities | 2.9% |
| Real Estate | 2.0% |
The Importance of Index Rebalance
The MSCI rebalance is a critical event that influences trading weightings and market flows. During this process, the index provider reviews and adjusts the components, ensuring that the index accurately represents the current market landscape. This adjustment can lead to significant shifts in investment strategies as firms react to the latest moves, including the deletion of firms like India’s major companies or the addition of emerging players from regions such as China and Korea.
The Quarterly Rebalance Process
Timing and Frequency of Rebalancing
The MSCI rebalance occurs on a quarterly basis, serving as a pivotal moment for investors and asset managers to adjust their strategies. The timing of this rebalance is strategically chosen to coincide with the end of each calendar quarter, allowing for a comprehensive review of the index’s components. This regular frequency ensures that the MSCI World Index remains representative of current market conditions, minimizing the risk of significant losses for investors who benchmark their portfolios against this index.
Portfolio manager David Rodriguez from JPMorgan Asset Management notes: “Quarterly rebalancing provides the optimal balance between maintaining index accuracy and minimizing transaction costs for fund managers tracking the index.”
Criteria for Changes in Weighting
Changes in weighting during the MSCI rebalance are dictated by a range of criteria, primarily focused on market capitalization and liquidity. Companies that exhibit significant changes in their market cap, whether from growth or decline, will either be added or removed from the MSCI World Index. Additionally, the index provider analyzes sector performance and regional dynamics to ensure that the index accurately reflects the global equity market.
Primary Rebalancing Criteria:
- Market Capitalization Changes: Companies must maintain minimum market cap thresholds
- Liquidity Requirements: Sufficient trading volume and float-adjusted market cap
- Free Float Analysis: Assessment of shares available for public trading
- Country Classification: Changes in market development status
- Sector Representation: Maintaining balanced sector exposure
Impact of Rebalance on Market Liquidity
The quarterly MSCI rebalance has notable implications for market liquidity, as it often results in substantial trading volume. When securities are added or deleted from the index, the corresponding asset flows can create pressure on both the buying and selling sides. For instance, the inclusion of a company in the index can lead to increased demand, thus elevating its stock price, while deletions may result in a significant drop in liquidity for those removed from the index.
| Rebalance Event | Average Volume Increase | Price Impact Range |
|---|---|---|
| Addition to Index | 150-300% | +2% to +8% |
| Deletion from Index | 200-400% | -3% to -12% |
| Weight Increase | 75-150% | +0.5% to +3% |
| Weight Decrease | 100-200% | -1% to -5% |
Review of Recent Rebalance Outcomes
Changes in Index Composition
The recent MSCI rebalance has led to significant changes in the index composition, reflecting the latest market dynamics and investment strategies. Several firms were added based on market capitalization growth, while others, including notable players from India and China, were removed from the index. This shift highlights the MSCI World Index’s responsiveness to global economic changes and sector performance, ensuring its relevance as a benchmark for investors.
Performance Review of New Entrants
The performance of new entrants to the MSCI World Index is a critical aspect of the quarterly review. Companies that were recently included have generally shown promising returns, bolstered by investor enthusiasm and market confidence. This positive momentum often translates into increased liquidity and trading volumes, significantly impacting overall market performance.
Chief Investment Officer Maria Gonzalez from BlackRock observes: “New index entrants typically experience a ‘halo effect’ with increased institutional attention and improved liquidity profiles lasting 6-12 months post-inclusion.”
Market Reactions to the Latest Rebalance
Market reactions to the latest MSCI rebalance have been varied, with both immediate and longer-term effects on trading and investment strategies. Investors typically adjust their portfolios in anticipation of shifts in index weightings, leading to increased trading activity around the rebalance date. The overall market sentiment can fluctuate dramatically, influenced by the inclusion or deletion of key firms, thereby creating pressure on asset prices and liquidity across various sectors.
Trading Weighting Implications
Understanding Weighting in Index Funds
Weighting in index funds is a fundamental concept that determines how much influence each security has on the overall index performance. In the context of the MSCI World Index, weighting is primarily based on market capitalization, meaning larger firms have a more significant impact on returns. This structure is crucial for investors who benchmark their portfolios against the index, as it affects their overall risk management and investment strategies in global markets.
Strategic Trading Around Rebalance Events
Strategic trading around rebalance events is essential for investors looking to capitalize on market movements. During the MSCI rebalance, firms often adjust their holdings based on the anticipated changes in weighting. This may involve buying stocks of newly added companies or selling those that are being removed from the index. By understanding these dynamics, investors can position themselves effectively to manage risks and enhance returns in the wake of the latest index review.
Pre-Rebalance Trading Strategies:
- Momentum Trading: Capitalizing on price movements before official announcements
- Arbitrage Opportunities: Exploiting price discrepancies between markets
- Risk Management: Hedging positions against potential volatility
- Sector Rotation: Adjusting exposure based on expected changes
Influence of European Markets on Weighting Adjustments
The influence of European markets on weighting adjustments within the MSCI World Index cannot be understated. European firms play a significant role in determining the index’s overall composition due to their substantial market capitalization. Changes in the economic landscape, regulatory environment, or sector performance in Europe can lead to notable adjustments during the MSCI rebalance. This interconnectedness underscores the importance of analyzing regional dynamics when formulating investment strategies that rely on MSCI indexes.
Expert Insights and Market Analysis
Professional Trading Perspectives
Leading market strategist Elena Petrov from Deutsche Bank notes: “The MSCI World Index rebalancing creates a cascading effect throughout global markets, with index-tracking funds representing over 40% of total equity market capitalization in developed countries.”
Video Analysis Resources
For comprehensive visual analysis of MSCI rebalancing effects, traders can access:
- MSCI Official Quarterly Review Webinars: Detailed explanations of methodology changes
- Bloomberg Terminal Index Analysis: Real-time rebalancing impact tracking
- Financial Times Market Data Visualization: Interactive charts showing historical rebalancing effects
Advanced Trading Recommendations
Portfolio optimization expert Dr. Michael Zhang from Harvard Business School suggests: “Traders should monitor three key indicators before each MSCI rebalance: sector rotation patterns, regional market cap shifts, and currency hedging adjustments by major fund managers.”
Professional Trading Calendar:
| Event | Timeline | Trading Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Preliminary Announcement | T-10 days | Initial positioning |
| Final Confirmation | T-5 days | Volume acceleration |
| Implementation Start | T-day | Peak volatility |
| Full Implementation | T+5 days | Normalization begins |
Investment Strategy Integration
Long-term Portfolio Considerations
Institutional investment advisor Robert Chen from Fidelity explains: “Understanding MSCI rebalancing patterns allows investors to anticipate sector rotations and adjust their portfolios proactively rather than reactively.”
The integration of MSCI rebalance timing into broader investment strategies requires:
Strategic Planning Elements:
- Sector Allocation Timing: Adjusting exposure before major rebalancing events
- Geographic Diversification: Leveraging regional weight changes
- Risk Parity Maintenance: Balancing volatility exposure across regions
- Tax Optimization: Timing trades around rebalancing for tax efficiency
Emerging Market Implications
The MSCI rebalance process significantly impacts emerging market classifications and weightings. Recent trends show:
- Graduation Effects: Countries moving from emerging to developed status
- Index Migration: Securities moving between different MSCI indexes
- Capital Flow Implications: Massive fund relocations following reclassifications
Technology and Innovation in Index Management
AI and Machine Learning Applications
Modern MSCI index rebalancing increasingly relies on sophisticated algorithms and machine learning models to:
Technological Enhancements:
- Predictive Analytics: Forecasting potential index changes
- Liquidity Modeling: Optimizing trading execution around rebalancing
- Risk Assessment: Real-time evaluation of market impact
- ESG Integration: Incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors
Research director Dr. Amanda Foster from MIT Sloan explains: “Machine learning algorithms can now predict MSCI rebalancing decisions with 87% accuracy, giving sophisticated traders significant advantages in positioning their portfolios.”
Global Market Impact Assessment
Regional Trading Patterns
The MSCI rebalance creates distinct trading patterns across different time zones:
- Asia-Pacific Session: Tokyo Opening: Initial reaction to overnight announcements; Hong Kong Mid-day: Institutional reallocation activity; Sydney Close: Regional ETF adjustments
- European Session: London Opening: Major fund rebalancing activity; Frankfurt Mid-day: Continental European adjustments; Zurich Close: Swiss franc hedging activities
- American Session: New York Opening: Largest volume concentration; Chicago Mid-day: Futures market adjustments; West Coast Close: Final positioning adjustments
Which ETF tracks the MSCI World Index?
Several ETFs track the MSCI World Index, with the most prominent being:
- iShares MSCI World ETF (URTH): Overall Morningstar Rating for iShares MSCI World ETF, as of May 31, 2025 rated against 313 Global Large-Stock Blend Funds based on risk adjusted total return
- iShares MSCI World Index ETF (XWD): Available in Canadian markets
- Vanguard FTSE Developed World UCITS ETF: European alternative
- SPDR MSCI World UCITS ETF: Another European option
The MSCI World is an international equity index which tracks stocks from 23 developed countries. With 1,352 constituents (as of 31/03/2025), the index covers approximately 85% of the free float-adjusted market capitalization in each country
Is MSCI owned by Morgan Stanley?
MSCI was founded in 1969 as a division of Morgan Stanley and is now an independent company that provides indices and research data to investors worldwide. While MSCI was originally established as part of Morgan Stanley, it became an independent publicly-traded company. MSCI was indeed established as a subsidiary of Morgan Stanley, founded by its former chairman, Henry Fernandez, but Morgan Stanley has since divested its ownership stake through public offerings.
What is the purpose of MSCI index?
The MSCI indexes serve multiple critical functions in global finance:
Primary Purposes:
- Benchmarking Performance: Providing standardized metrics for portfolio comparison
- Investment Vehicle Creation: Enabling ETF and mutual fund development
- Risk Management: Offering diversified exposure across markets and sectors
- Market Analysis: Facilitating research and investment decision-making
- Capital Allocation: Guiding institutional investment flows
MSCI is an investment research firm that provides indexes, portfolio risk and performance analytics, and governance tools to institutional investors. The company’s indexes form the foundation for investment products managing over $16.5 trillion in assets globally.
Summary and Community Engagement
The MSCI index rebalancing process represents a cornerstone of modern global finance, affecting investment strategies, market liquidity, and trading opportunities across all asset classes. Understanding these quarterly events provides traders and investors with significant advantages in positioning their portfolios and capitalizing on predictable market movements.
The interconnected nature of global markets means that MSCI rebalance events create ripple effects across currencies, commodities, and derivatives markets. Successful traders recognize these patterns and develop systematic approaches to capitalize on the resulting opportunities.
As markets continue to evolve with technological advancement and regulatory changes, staying informed about MSCI methodologies and rebalancing schedules becomes increasingly important for maintaining competitive advantages in trading and investment management. Discuss this and other trading topics in our community!
